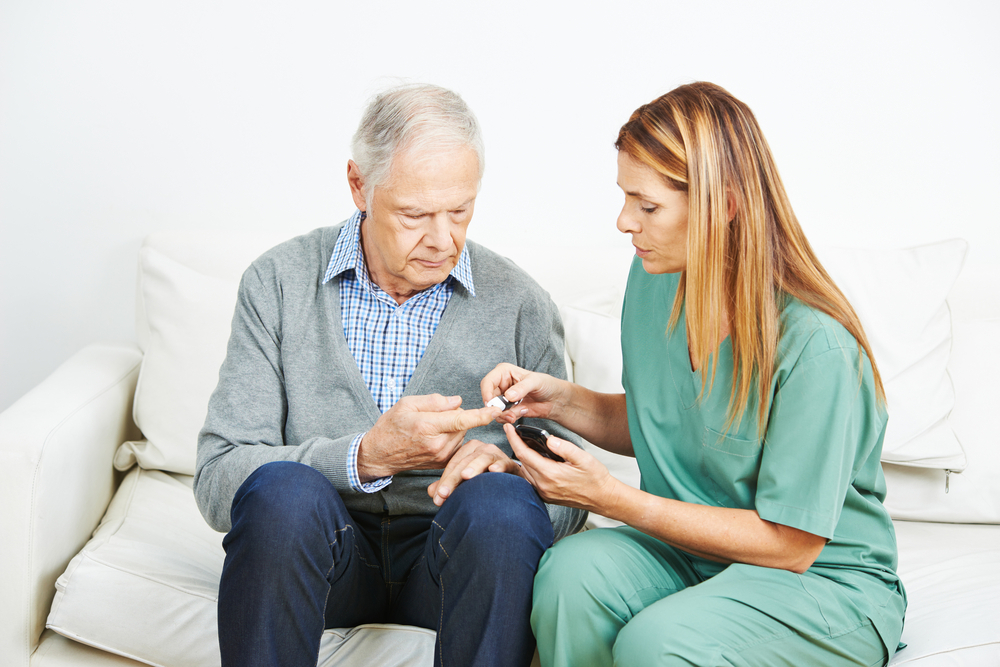
- Pakwellness
- 0 Comments
Introduction:
Diabetes, a chronic metabolic disorder, affects millions worldwide due to the body’s inability to produce or utilize insulin effectively. In this comprehensive blog post, we delve into the intricacies of diabetes, exploring its various types, common symptoms, and available treatment options. By enhancing our understanding of this condition, we can empower individuals and communities to effectively manage diabetes and lead healthier lives.
Types of Diabetes:
1. Type 1 Diabetes:
Type 1 diabetes, commonly known as insulin-dependent diabetes, stems from an autoimmune response that attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. Typically diagnosed in childhood or early adulthood, individuals with type 1 diabetes require lifelong insulin injections to regulate blood sugar levels.

2. Type 2 Diabetes:
Type 2 diabetes, the most prevalent form, arises when the body becomes resistant to insulin or fails to produce sufficient amounts to maintain proper blood sugar control. Lifestyle factors such as poor diet, sedentary habits, and obesity contribute to type 2 diabetes, which can develop at any age but is more common among adults.

3. Gestational Diabetes:
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and affects some women who have no prior history of diabetes. It typically manifests between the 24th and 28th week of pregnancy but typically resolves after childbirth. Women who experience gestational diabetes are at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
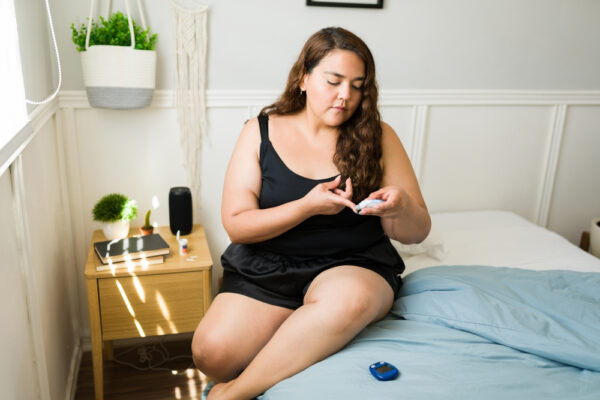

Common Symptoms of Diabetes:
Recognizing the symptoms of diabetes is crucial for early detection and timely intervention. Some prevalent symptoms include frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, increased hunger, fatigue and weakness, blurred vision, slow-healing wounds or frequent infections, and tingling or numbness in the hands or feet.

Treatment Options:
Managing diabetes effectively involves a multifaceted approach. The blog covers several essential treatment options, including:
1. Lifestyle Modifications:
Emphasizing the significance of healthy lifestyle choices, we explore how adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, achieving and maintaining a healthy weight, and managing stress levels can positively impact diabetes management, particularly for type 2 diabetes.

2. Medications:
Various oral medications and injectable drugs are available for individuals with type 2 diabetes to regulate blood sugar levels. These medications work by improving insulin sensitivity, reducing glucose production, or stimulating insulin release. For individuals with type 1 diabetes, insulin therapy remains a vital component.
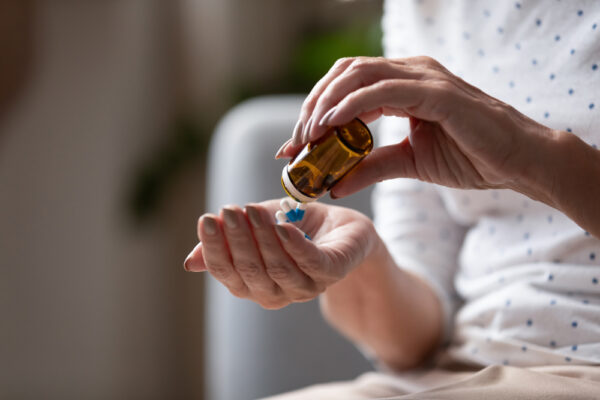

3. Blood Sugar Monitoring:
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels plays a pivotal role in managing diabetes. By utilizing blood glucose meters or continuous glucose monitoring systems, individuals can track their blood sugar levels, observe patterns, and make informed decisions regarding their diet, exercise, and medication management.
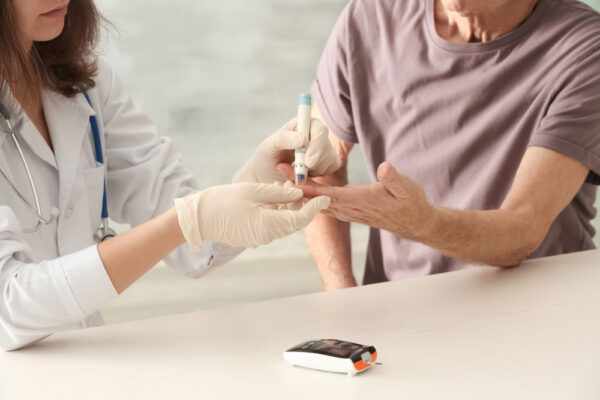
4. Insulin Therapy:
Various oral medications and injectable drugs are available for individuals with type 2 diabetes to regulate blood sugar levels. These medications work by improving insulin sensitivity, reducing glucose production, or stimulating insulin release. For individuals with type 1 diabetes, insulin therapy remains a vital component.
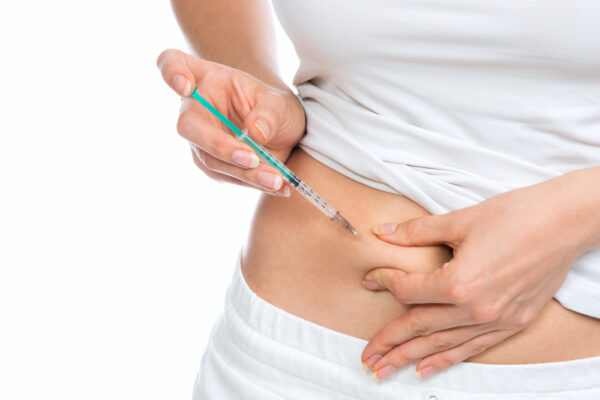
5. Diabetes Education and Support:
Insulin therapy is crucial for individuals with type 1 diabetes and may also be prescribed for those with type 2 diabetes when other treatments prove insufficient. This section discusses various insulin delivery methods, such as injections using syringes, pens, or insulin pumps, to provide comprehensive information on effective insulin usage.

Conclusion:
The blog concludes by emphasizing the chronic nature of diabetes and the importance of comprehensive management. By deepening our understanding of the various types of diabetes, recognizing symptoms, and exploring treatment options, individuals can proactively manage their condition. Early diagnosis, adopting a healthy lifestyle, adhering to prescribed medications, regular blood sugar monitoring, and seeking ongoing education and support are fundamental steps towards effective diabetes
